If you are looking for ways to incorporate fish into your diet, two popular choices are sardines and tuna. Both types of fish are conveniently canned and easy to take with you wherever you go. But this is where the similarities start to differ.
Sardines are small fish, typically measuring between 6 to 12 inches in length and weighing less than one pound. Tuna, on the other hand, can get quite large. Tuna can range in length from 1 to 15 feet long and weigh anywhere from 3 to 1,500 pounds!

In this article, I want to explore further the similarities and differences between these two fish. I also want to look at the nutritional content of each fish as well as any ecological impacts and see if one fish is a healthier choice than the other.
Serving sizes for sardines and tuna differ so I will be doing a more accurate weight-for-weight comparison of 100g each. I will also be comparing canned sardines and tuna which are packed in oil. The oil helps to preserve the natural oils of the fish and helps lessen any fishy taste.
Ingredient Comparison
When comparing sardines and tuna, it’s important to note their nutritional differences to determine which fish is the better choice for your diet.
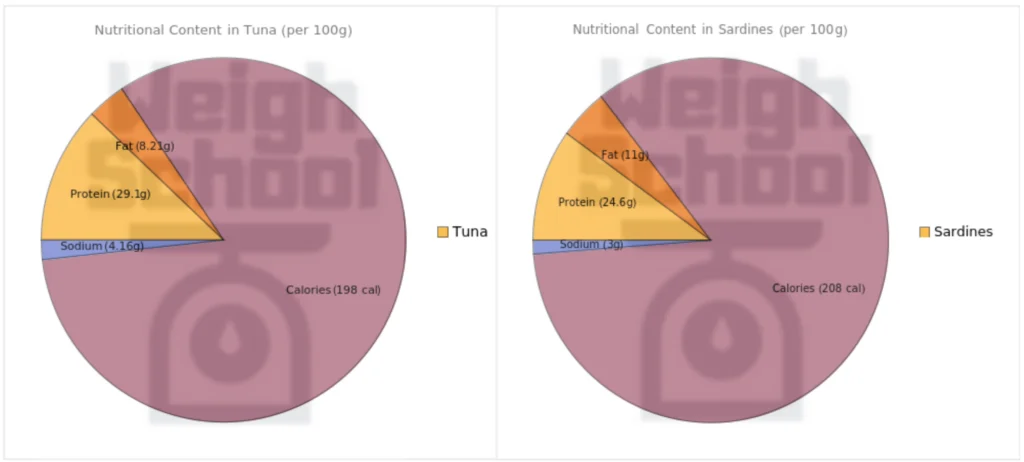
Protein: Sardines and tuna are a good choice if you are looking to increase your protein intake. Both are a high-protein food but tuna has a slightly higher protein content. A 100g serving of tuna has 29.1g of protein and sardines have 24.6g.
Fat Content: Sardines have a higher fat content compared to tuna, with an average of 11g per 100g serving. On the other hand, canned tuna has an average of 8.21g of fat per serving. If you are concerned about the fat content, you can opt to buy tuna that is canned in water and sardines that have been canned in tomato sauce.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Both sardines and tuna contain omega-3 fatty acids which support brain function and combat cardiovascular issues.
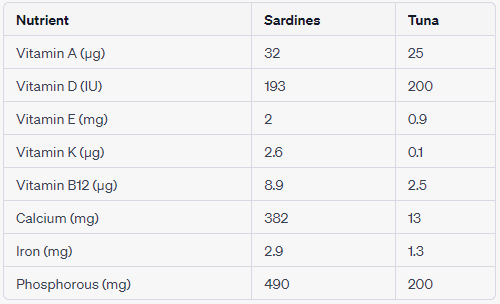
Vitamins: Both sardines and tuna are nutritional powerhouses but sardines have a higher concentration of each vitamin and mineral than tuna. Sardines are high in calcium, iron, phosphorous, potassium, vitamins A and D, and vitamin B12, just to list a few.
In summary, when comparing sardines and tuna based on their ingredients, consider the following:
- Protein: Tuna has slightly more protein than sardines.
- Fat Content: Sardines have a higher fat content than tuna in general.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Both fish contain beneficial omega-3 fatty acids.
- Vitamins: Tuna has a more versatile vitamin profile, while sardines have higher levels of vitamins D and E.
Ultimately, the choice between sardines and tuna will depend on your personal preferences and dietary needs. Both fish offer health benefits and can be a valuable addition to your diet.
Nutritional Comparison
Best for Calorie Content
When comparing sardines and tuna in terms of calorie content, tuna is the better option for those looking to consume fewer calories. A 100g (3.5 oz) portion of sardines has an average of 208 calories, while the same portion size of tuna contains 198 calories.
Best for Carbs & Sugar Content
Both sardines and tuna have zero amounts of carbs and sugar, making them suitable options for low-carb diets. They are both good sources of protein and healthy fats.
Best for Protein Content
Tuna comes out on top in terms of protein content. A 100g serving of canned tuna provides 29 grams of protein, while the same portion size of canned sardines, packed in oil, provides 24.6 grams of protein. Your body can use this protein to fight infection and maintain lean muscle tissue.
Best for Fat Content
Sardines contain more healthy fats compared to tuna. Both fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support brain function and combat cardiovascular issues. However, due to the higher fat content, sardines also have a higher caloric profile.
Best for Fiber Content
Fish, in general, do not contain dietary fiber, so neither sardines nor tuna are sources of fiber. You can increase the fiber content of the fish by pairing it with a vegetable or other high-fiber food.
Best for Sodium/Salt Content
Canned fish, such as sardines and tuna, can contain varying amounts of sodium, depending on the product and how they are packaged. A 100g serving size of sardines has around 300g of sodium. The same serving size of tuna has 416g of sodium.
It’s essential to check the labels for each brand’s sodium content to make an informed decision on the best option for you.
Best for Vitamins/Minerals
Tuna has a more versatile and richer vitamin profile when compared to sardines. Sardines are richer in B vitamins as well as vitamin A. On the other hand, tuna is richer in vitamins D and K. Vitamin K is important for blood clotting and healthy, strong bones.
Best for Flavor/Texture

When it comes to flavor, you’ll find that sardines and tuna offer distinct taste profiles. Sardines have a rich, umami flavor that is amplified by their soft texture. They are typically sold canned in oil, which further enhances their flavor and reduces the fishy taste and smell.
Tuna, on the other hand, is not fishy and has a meatier yet mild flavor profile. Depending on the type, canned tuna can have different textures, ranging from flaky to firm. Yellowfin and albacore tuna typically have a firm, steak-like texture, while skipjack and light canned tuna are more flaky and tender.
When it comes to texture differences, consider the following:
- Sardines: Soft, rich, and oily
- Tuna: Ranging from flaky to firm, depending on the type
If you enjoy versatile options and a less pronounced fishy taste, tuna might be your preference when it comes to flavor and texture. However, if you appreciate a strong, rich taste with a soft texture, go for sardines. Ultimately, it depends on your personal preference and how you plan to use the fish in your recipes.
Health Benefits
When comparing sardines and tuna, it is essential to consider the health benefits that these two fish offer. Both are excellent sources of protein and omega-3 fatty acids, important nutrients to support overall health and well-being. However, there are some nutritional differences between the two.
Protein
Protein is necessary for the growth and maintenance of lean muscle tissue, as well as supporting a healthy immune system. A 100 g serving of canned sardines, packed in oil, offers 24.6 grams of protein, while the same amount of canned tuna provides 29 grams. With both options being rich in protein, incorporating them into your diet can help you meet your daily protein needs.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for optimal brain function and heart health. Both sardines and tuna are great sources of these healthy fats. Incorporating either one of these fish into your diet can help increase your omega-3 intake, which is beneficial for overall health.
Vitamins and Minerals
Sardines and tuna are both powerhouses of nutrition but they do differ in some areas. Because sardines contain edible bones, it is much higher in calcium than tuna. A 100g serving of sardines contains 30 times more calcium than tuna.
Tuna is rich in vitamins D and K, which help the immune system, boost your mood, lower your risk of diabetes and heart disease, and help build strong bones.
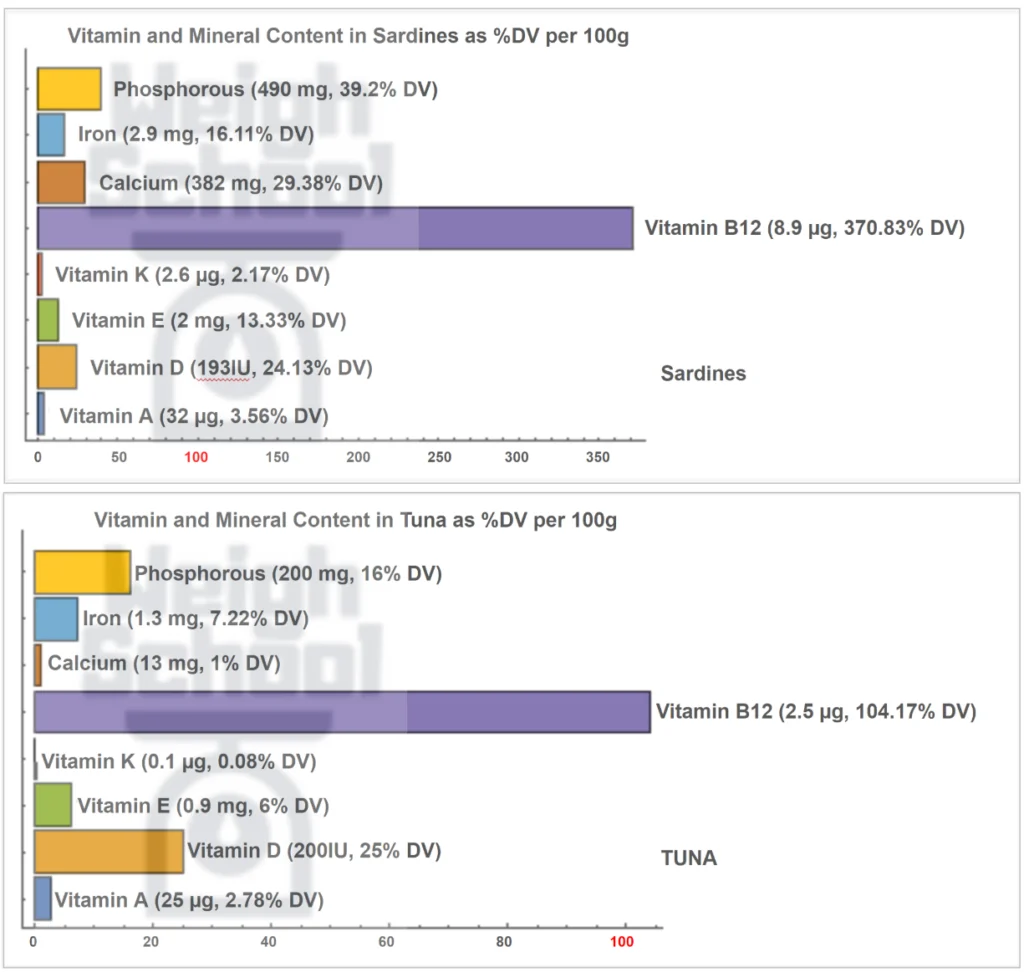
Data of the above vitamin and mineral visualization

Caloric Profile
While both sardines and tuna are nutritious options, they do differ in calorie content. Due to its higher fat content, a 100-gram portion (3.5 ounces) of sardines contains approximately 208 calories, whereas the same serving size of tuna provides around 198 calories. Depending on your calorie needs, you may choose either fish based on their caloric profiles.
In summary, both sardines and tuna offer numerous health benefits, with some nutritional differences. By incorporating them into your diet, you can enjoy the advantages of their protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins and minerals.
Allergies and Sensitivities
When considering sardines and tuna, it’s important to be aware of your personal allergies and sensitivities. While both fish are nutritious choices for your diet, they may cause issues if you have a food allergy or intolerance.
A food allergy involves your immune system and can cause life-threatening symptoms. Symptoms of a food allergy can include congestion, itching, hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, or anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening reaction. If you suspect you have a food allergy, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
On the other hand, food intolerance often results in digestive issues, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea. This type of reaction does not involve your immune system, but it can still be uncomfortable and problematic when incorporating these fish into your diet.
It’s important to pay attention to your body’s reactions when consuming sardines or tuna. If you experience any new symptoms after eating sardines or tuna, consult your healthcare provider right away to see whether or not you have an allergy or sensitivity to either of these fish.
It’s also important to read the nutrition label if you have any other food allergies or sensitivities, such as gluten or soy. Sardines and tuna may be processed in a facility where these allergens are present and cross-contamination could happen.
Being diligent about your choices can help you avoid potential negative reactions and make the most of the health benefits offered by sardines and tuna.
Best for Price
When it comes to price, you’ll generally find that sardines are a more affordable option compared to tuna. Sardines tend to be cheaper because they’re lower on the food chain, more abundant, and have a shorter life cycle, leading to a quicker replenishment of their populations.
In contrast, tuna are larger and have a longer life cycle, causing their populations to be more vulnerable to overfishing. This can lead to higher prices for consumers due to the potential scarcity of fish.
While shopping for sardines and tuna, you should remain aware of the origins of the fish you’re buying. Look for products that have been sustainably sourced or certified by an organization like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), which ensures that the fish is harvested in an ecologically responsible manner.
In summary, sardines generally offer a more cost-effective option compared to tuna, while still providing numerous nutritional benefits. For those looking to not only save money but also make more environmentally conscious decisions, sardines often make the better choice.
Overall Winner – Which One is Better?
Top 5 Similarities:
- Both sardines and tuna are rich sources of protein, which is essential for muscle building and repair.
- Both contain essential vitamins such as Vitamin B12, which is vital for maintaining healthy nerve cells and producing DNA, and Vitamin D, which helps in calcium absorption for bone health.
- Both sardines and tuna contain a significant amount of Omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to benefit heart health.
- Both are sources of essential minerals like iron, which is necessary for transporting oxygen in the blood, and zinc, which supports immune function and wound healing.
- Both sardines and tuna have cholesterol content, which is necessary in small amounts for building cell membranes and hormone production.
Top 5 Differences:
- Sardines contain a higher amount of calcium (240 mg) compared to tuna, making them a better source for supporting bone health.
- Sardines have a higher Vitamin E content (1.38 mg) compared to tuna, which is an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage.
- Sardines have a higher cholesterol content (61 mg) compared to tuna (36 mg), which might be a consideration for individuals monitoring their cholesterol intake.
- Sardines contain carbohydrates (0.54 g), including dietary fiber (0.1 g) and sugars (0.43 g), whereas the carbohydrate content in tuna is not specified in the USDA website.
- Sardines contain a higher amount of total fat (10.4 g) compared to tuna, which includes both saturated and unsaturated fats that are necessary for energy and supporting cell growth.
When comparing sardines and tuna, it’s essential to consider your preferences and nutritional needs. Both fish offer their distinct benefits, so let’s dive into the details.
In terms of protein, tuna does come out ahead. A 6-ounce portion of canned tuna contains 29 grams of protein, while an equivalent portion of canned sardines (packed in oil) provides almost 25 grams of protein. This difference is helpful to note if you’re seeking to increase your protein intake, which aids in lean muscle maintenance and infection-fighting.
However, sardines have a higher fat content, providing more calories than tuna—208 calories in 100 g of sardines compared to 198 calories in 100 g of tuna. Although this difference is not significant, it’s worth considering if you’re counting calories.
Both fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support brain function and cardiovascular health. However, they vary in their vitamin profiles.
Sardines are richer in vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B12, and A. In contrast, tuna is richer in vitamins D and K. If you’re aiming to boost specific vitamin intakes, this information can guide your choice.
Sardines are often seen as an alternative to tuna in recipes, partially due to their lower cost and health benefits. While tuna is more popular, incorporating sardines into your meals can contribute positively to your health goals.
In summary:
- Protein: Tuna wins
- Calorie content: Tuna wins (lower calories)
- Omega-3s: Tie
- Vitamin profile: Depends on your needs (sardines for B vitamins and A, tuna for D and K)
- Cost: Sardines win
So, as you can see, both fish have their merits, and the decision ultimately comes down to your individual preferences and nutritional goals. Experiment with each type of fish and see which one you and your family prefer.
Related Articles
Sardines vs Anchovies (Complete Comparison)
